Anatomy of a Home Septic System
July 4, 2023
PLEASE NOTE: We do not currently service septic systems.
However we'd be happy to recommend a few companies if you reach out to us.
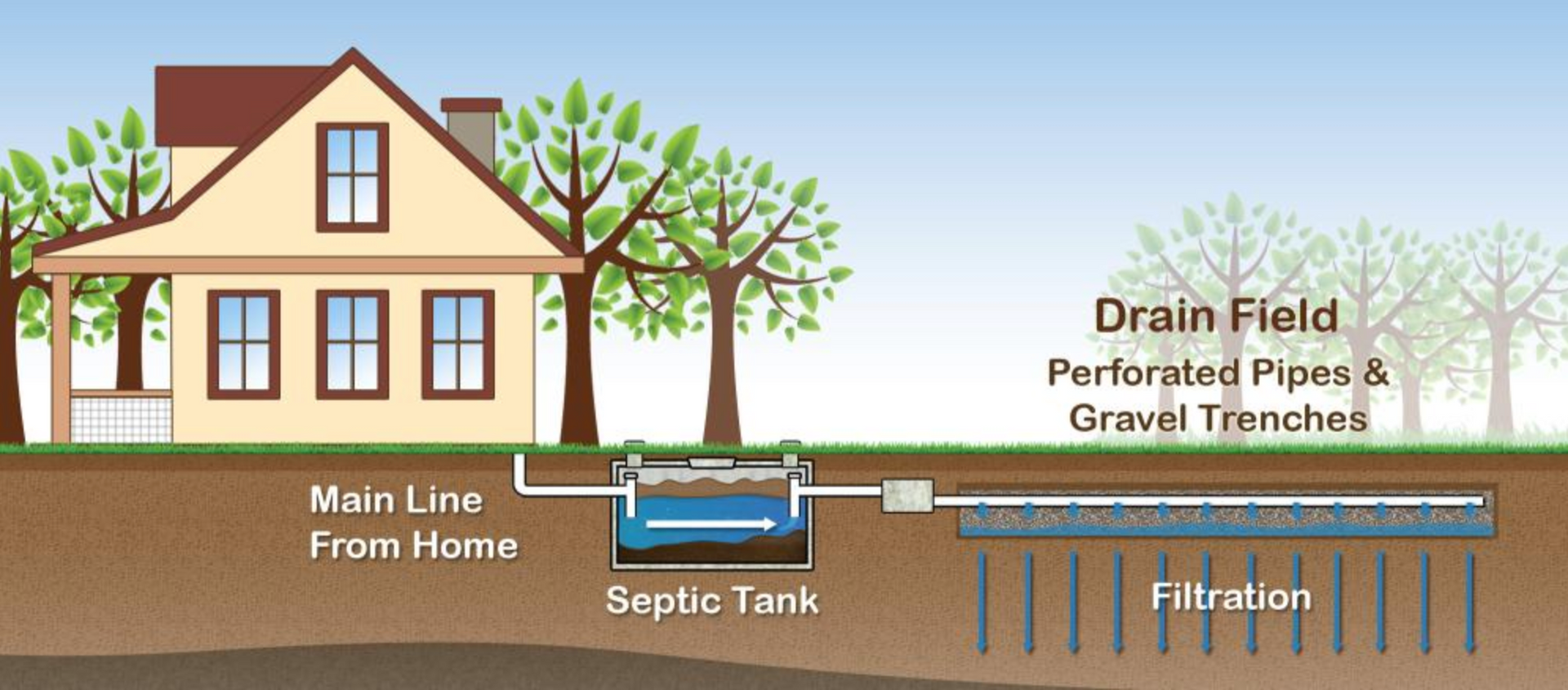
While hidden from plain sight, a home septic system plays a crucial role in effectively managing and treating wastewater from residential properties. Understanding the anatomy of a septic system can help homeowners maintain its functionality and prevent potential issues. In this article, we'll take a closer look at the essential components that make up a typical home septic system and explore how they work together to keep our environment clean and healthy.
Septic Tank
At the core of a septic system lies the septic tank, a buried, watertight container made of concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene. The primary function of the septic tank is to receive and separate the incoming wastewater. It acts as a preliminary treatment chamber, allowing solid waste to settle at the bottom and scum to float on the surface, while the clarified liquid flows out into the drain field for further treatment.
Inlet and Outlet Pipes
The septic tank is connected to the house through an inlet pipe, which carries all the wastewater from various household sources such as toilets, showers, sinks, and washing machines. This pipe directs the incoming wastewater into the septic tank, where the separation process begins.
On the other end of the septic tank, an outlet pipe allows the clarified liquid, known as effluent, to exit the tank and flow towards the drain field for further treatment and absorption into the soil.
Baffle
Inside the septic tank, a baffle is placed near the inlet pipe to prevent the immediate release of solids and scum into the drain field. It ensures that the wastewater has enough time to undergo primary treatment, allowing the heavier solids to settle at the bottom while the lighter scum floats to the top.
The baffle also helps to prevent any floating scum from escaping into the outlet pipe, ensuring that only the clarified effluent is discharged into the drain field.
Drain Field
The drain field, also known as the leach field or absorption field, is a vital component of the septic system responsible for the final treatment and disposal of the effluent. It consists of a network of perforated pipes buried in trenches or beds, usually filled with gravel or another suitable medium.
Once the effluent leaves the septic tank, it enters the drain field and is slowly released into the surrounding soil. Through a process called soil percolation, the soil acts as a natural filter, further treating the effluent by removing harmful bacteria, viruses, and nutrients. The treated wastewater then reenters the groundwater system or is evaporated.
Soil
The soil composition and characteristics play a critical role in the effectiveness of the drain field. Ideally, the soil should have good absorption and percolation qualities to facilitate the efficient filtration and treatment of the effluent. Different types of soil, such as sandy or loamy soil, have varying percolation rates, and the suitability of the soil for a septic system depends on regional factors and soil testing.
Maintenance and Care
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of a home septic system, regular maintenance and care are essential. Here are a few key practices to keep in mind:
Regular Pumping:
Schedule periodic septic tank pumping to remove accumulated solids and prevent blockages. The frequency depends on household size, tank capacity, and water usage patterns.
Water Conservation: Implement water-efficient practices and avoid overloading the septic system. Fix leaks promptly, install low-flow fixtures, and spread out water usage throughout the day.
Proper Waste Disposal:
Avoid flushing non-biodegradable items, chemicals, grease, medications, or excessive amounts of household cleaners down the drain, as they can harm the septicsystem and hinder its performance.
Protect the Drain Field:
Avoid driving or parking vehicles, constructing buildings, or planting trees with extensive root systems over the drain field to prevent damage to the pipes and soil absorption capacity.
Regular Inspections:
Have a professional inspect your septic system regularly to identify any potential issues early on and ensure its proper functioning.
Conclusion
A home septic system is an integral part of residential wastewater management, providing a safe and effective means of treating and disposing of household wastewater. Understanding the anatomy and function of a septic system empowers homeowners to take proactive measures in maintaining its efficiency and preventing potential problems. By following proper maintenance practices and caring for each component, homeowners can ensure the longevity and reliable performance of their septic system, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
You might also like
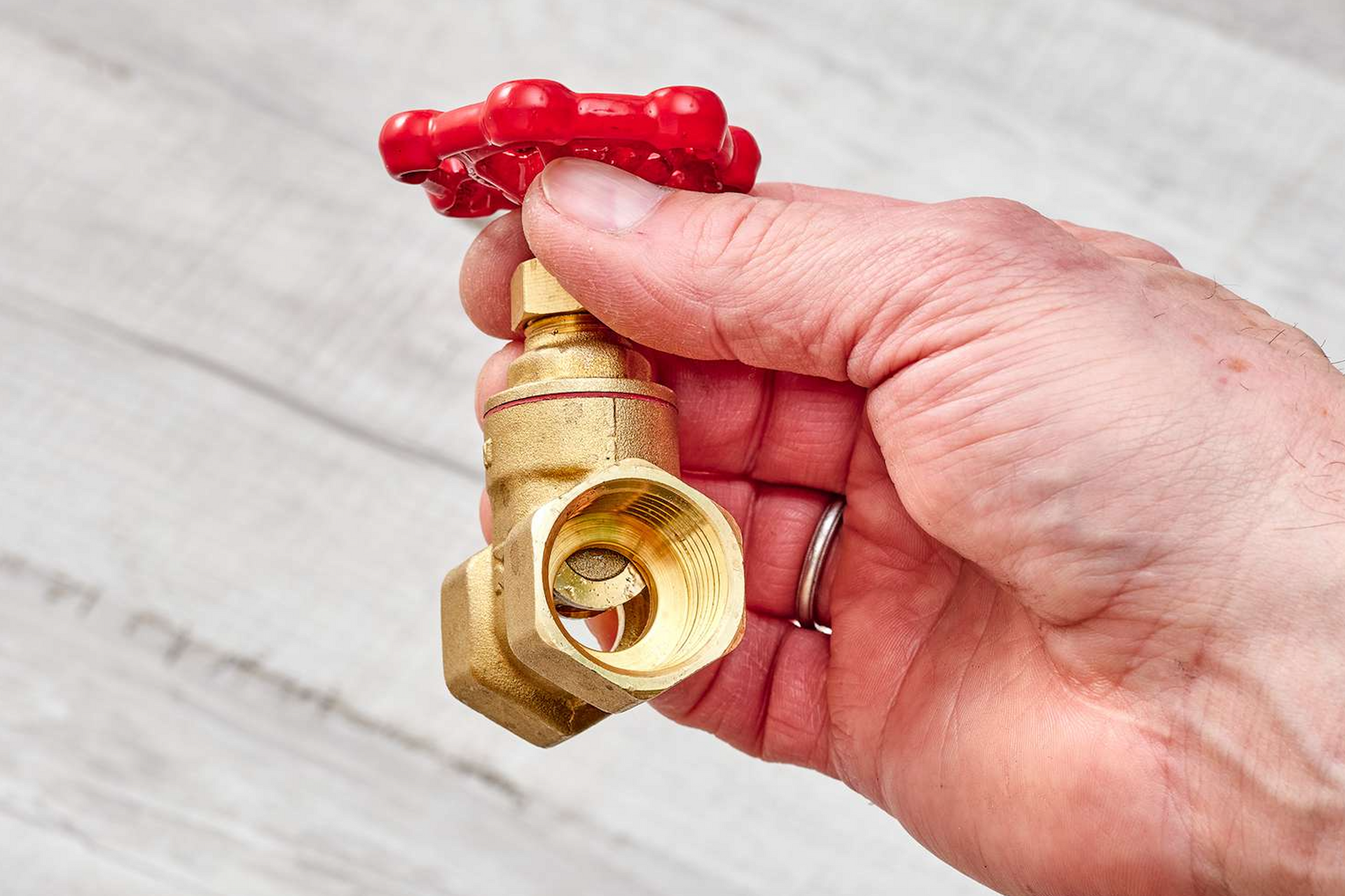

As the trusted experts at Aaron's Water Heaters, we understand the importance of a reliable residential water heater, especially during those chilly Michigan winters. Today, we want to dive into a crucial aspect of your water heating system that often goes unnoticed – the valves. Specifically, we'll be comparing ball valves and gate valves, shedding light on their differences and helping you make an informed decision for your replacement water heater installation. The Basics: Before we delve into the specifics of ball and gate valves, let's briefly go over their primary functions. Valves play a pivotal role in controlling the flow of water within your plumbing system. They act as gatekeepers, allowing you to shut off or regulate the water supply to different parts of your home. Ball Valves: Ball valves are recognized for their simplicity and efficiency. They feature a spherical disc inside the valve body, which can be rotated to control the flow of water. When the handle is perpendicular to the pipe, the valve is closed, and when it's parallel, the valve is open. This straightforward design allows for quick and precise control over the water flow, making ball valves a popular choice for many residential applications. Advantages of Ball Valves: * Quick and Easy Operation: Ball valves are known for their user-friendly operation, allowing homeowners to shut off the water supply rapidly in case of emergencies or maintenance. * Durability: The design of ball valves makes them less prone to leaks, ensuring a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance requirements.
* Reliability: Ball valves provide a tight seal, minimizing the risk of water wastage and maintaining a consistent water flow. Gate Valves: Gate valves, on the other hand, employ a flat or wedge-shaped gate that moves up and down within the valve body. When the gate is raised, water can flow through; when lowered, the valve is closed. While gate valves are also widely used, they differ from ball valves in terms of operation and application. Advantages of Gate Valves: * Full Flow Control: Gate valves offer full, unrestricted flow when fully open, making them suitable for applications where maximum water flow is essential.
* Less Susceptible to Clogs: The straightforward design of gate valves makes them less prone to clogging, ensuring consistent performance over time. Choosing the Right Valve for Your Water Heater (and other plumbing in your home): When it comes to selecting the right valve for your residential water heater in here in Michigan, several factors come into play. Consider the specific requirements of your system, your preferences for ease of use, and the overall functionality you desire. For most homeowners in our region, the simplicity and reliability of ball valves make them an excellent choice. However, if your water heater demands high water flow and you prioritize maximum control, a gate valve might be the better fit. Conclusion: At Aaron's Water Heaters, we prioritize not only delivering top-notch replacement water heater installations but also ensuring you understand the components of your plumbing system. Knowing the difference between ball and gate valves empowers you to make informed decisions for your home. Contact Aaron's Water Heaters today for expert advice and seamless water heater installations tailored to the unique needs of fellow Michigan homeowners. Stay warm and worry-free with Aaron's!

Water heaters play a crucial role in our daily lives, providing us with hot water for showers, cleaning, and various household tasks. While they are essential, it's important for homeowners to be aware of potential safety hazards associated with water heaters. In this article, we will discuss key aspects of water heater safety and offer tips to ensure your system operates smoothly without posing risks to your home and family. Temperature Settings: One of the first considerations for water heater safety is setting the temperature at an appropriate level. The U.S. Department of Energy recommends a temperature setting of 120°F to prevent scalding while still meeting the needs of most household activities. Higher temperatures can increase the risk of burns, especially for children and the elderly. Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance is essential for the safe and efficient operation of your water heater. Over time, sediment can accumulate at the bottom of the tank, reducing its efficiency and potentially causing overheating. Schedule annual flushing of the tank to remove sediment buildup and ensure optimal performance. Pressure Relief Valve: Every water heater is equipped with a pressure relief valve as a safety measure. This valve releases excess pressure from the tank, preventing potential explosions. Homeowners should test this valve periodically to ensure it is functioning correctly. If you find any issues, contact a professional plumber to address the problem promptly. Proper Ventilation: Gas-powered water heaters require proper ventilation to ensure the safe expulsion of combustion gases. Make sure the area around your water heater is well-ventilated and free from obstructions. Additionally, have a professional inspect the ventilation system annually to confirm its effectiveness. Check for Leaks: Water leaks around your water heater can lead to serious damage and pose safety risks. Regularly inspect the area around the heater for any signs of leakage, including rust or water puddles. Address any leaks promptly by tightening connections or replacing faulty components. Age of the Water Heater: Like all appliances, water heaters have a lifespan. Most units last around 10-15 years. If your water heater is nearing the end of its expected lifespan, consider proactively replacing it to avoid potential breakdowns and safety hazards associated with aging systems. Carbon Monoxide Detection: For gas water heaters, it's crucial to have a functioning carbon monoxide detector installed in the vicinity. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can be produced by gas-burning appliances. Regularly check your detector and replace the batteries to ensure it is operational at all times. Conclusion: Prioritizing water heater safety is a responsibility that every homeowner should take seriously. By following these essential tips and conducting regular inspections and maintenance, you can ensure your water heater operates efficiently and safely. If you ever have concerns or encounter issues beyond your expertise, don't hesitate to consult with a professional plumber to address the issue promptly. Your family's safety and the longevity of your water heater depend on proactive care and attention to these crucial details.

Ever wonder what that random bare wire is sticking out of the ground near your gas meter or along the foundation of your house? No, someone didn’t forget to connect it to a circuit. Its purpose is safety! Let us explain… The underground infrastructure of our cities and towns is complex, carrying everything from water and gas to electricity and communications. For those in industries such as plumbing, like us at Aaron's Water Heaters, understanding the nuances of this underground world is essential. One such nuance is the use of tracer wires, which play a critical role in locating and identifying these utilities. In Michigan, understanding the color code of these tracer wires is pivotal. Here's a dive into what each color signifies according to the Michigan building code. What are Tracer Wires? Before we delve into the color codes, it's crucial to understand what tracer wires are. They're conductive wires buried alongside underground utilities like water lines, gas lines, or other conduits. These wires make it possible to locate the utilities later using an electronic locator, preventing potential damage to the infrastructure and ensuring safety during any excavation or drilling. Michigan Building Code: Tracer Wire Colors and Their Meanings The Michigan building code adopts the APWA (American Public Works Association) Uniform Color Code for marking underground utilities. Each color represents a different type of utility. Let's break down the significance of each: Red: Electrical power lines, cables, conduit, and lighting cables. The presence of a red tracer wire usually indicates that there's an electrical utility underground. Caution is advised. Yellow: Gas, oil, steam, petroleum, or gaseous materials. Yellow is a warning color, indicating potential flammable and hazardous materials below. Orange: Communication, alarm or signal lines, and cables or conduit. This color is generally associated with telecommunication lines like phone, internet, or cable TV. Blue: Potable water. Blue tracer wires lead to clean drinking water sources, and it's essential not to contaminate these lines during any work. Purple: Reclaimed water, irrigation, and slurry lines. Purple indicates non-potable water, used mainly for irrigation or industrial purposes. Green: Sewers and drain lines. Green tracer wires typically show the pathways of waste and stormwater systems. White: Proposed excavation. This color isn't necessarily for a tracer wire but is used in marking to indicate a planned excavation site. Pink: Temporary survey markings. Again, pink might not be associated with a tracer wire directly, but it is important in the realm of excavation and utility mapping. Why is Respecting these Color Codes Important? Mistaking one utility for another can have catastrophic consequences. For example, puncturing a gas line while thinking it's a water line can lead to explosions. Additionally, not locating utilities before digging can result in costly repairs, disrupted services, and potential legal liabilities. Hence, respecting and understanding the color codes is paramount. Final Thoughts While Aaron's Water Heaters specializes in keeping your home's water heating systems optimal, we believe in a holistic understanding of all things related to home infrastructure. Knowledge of underground utilities and the importance of tracer wires is just one aspect of that. If you're undertaking any digging or excavation, always ensure you're aware of the tracer wire color codes in your region. Remember, safety always comes first. Stay informed and ensure any professionals you hire are knowledgeable about the local building codes and best practices. If you have any questions related to water heaters or associated plumbing, don't hesitate to get in touch with Aaron's Water Heaters. We're here to help!
